Seal away your teeth to protect them against cavities
What are dental sealants?
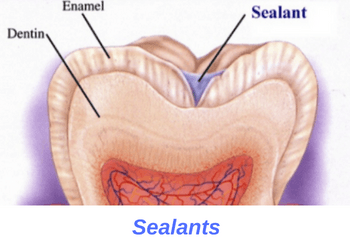
Dental sealants are tooth-colored, plastic coatings placed to protect teeth against cavities. Sealants are typically placed on baby teeth with deep groves to keep cavity bugs out. Dentists use sealants to protect molar baby teeth with deep groves. These teeth are particularly susceptible to developing cavities because it's hard for children to clean their back molar teeth. Placing a sealant on your tooth essentially seals off access to the inner tooth structure. The process is simple, painless, and takes just a few minutes to complete. Most dentists recommend that you consider placing sealants on your children's teeth to protect against cavities.
What is a sealant procedure like?
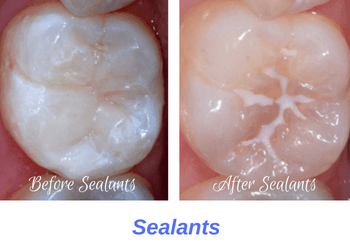
Placing sealants is a very simple procedure which is no more difficult than getting a routine dental cleaning. Unlike fillings, sealant do not require any sort of anesthesia or tooth structure removal. Plus, it only takes a few minutes to put sealants on your child's teeth, but the sealants help protect their teeth for years to come. Typically, we recommend placing sealants on the most distally positioned teeth. This is because children have a hard time cleaning these far positioned molar teeth. Most dentists recommend applying a set of dental sealants at about 6 to 7 years to your 1st molar teeth, and a second set of sealants at age 11 to 12 to your 2nd molar teeth. Some dentists only place sealants on adult molar teeth, others recommend applying sealants onto baby teeth as well. Regardless, we highly recommend that you consider placing sealants to protect your child's teeth against cavities.
What are the benefits of placing sealants on baby teeth?
Sealants have been proven very effective in fighting off cavity bugs, especially in children. Placing sealants on your teeth can help you avoid more serious problems down the line. Here are some of the benefits of placing sealants on your teeth:
Reduced risk of cavities
The main purpose of dental sealants is to protect children's teeth against dental cavities. Deep groves on the back molar teeth are very susceptible to developing cavities. This, combined with the fact that children eat more sugars and don't brush their back teeth, can be a recipe for disaster. The alternative to placing sealants would be to wait and see if these teeth develop cavities. However, should this happen, you now require a filling or possibly a root canal treatment. Placing a dental sealant is much easier, safer, and more economical. Plus, sealant visits are virtually painless. Unfortunately, the same can not be said of fillings or root canal procedures!
Creating a positive dental experience
Another benefit of dental sealants is that they create a positive dental experience for children. If your child’s first visit for invasive dental work involves needles and pain, this could lead to an everlasting fear of the dentist. On the opposite hand, a 15-minute pain-free sealant appointment is an excellent way of introducing your child to the dentist. This helps your child overcome his or her fear of the dentist to create a good relationship with their dentist.
Are there any risks with placing dental sealants on teeth?
There are absolutely no risks whatsoever with placing dental sealants on your teeth. Placing sealants is simple, easy, and pain-free. Plus, dental sealants are fully reversible, since there's no actual tooth removal involved. This means that sealants do no harm to your teeth. Typically, sealants stay on your teeth, protect them for several years, and slowly dissolve away. By the time you’re an adult, your sealants have typically vanished, having served their purpose.
Dental sealants in San Clemente, Orange County

Schedule your appointment with us today to learn more about dental sealants. Call us at (949)481-2540 or book your appointment online today. Our dentist, Dr. Jazayeri, will examine your child's teeth to determine if he or she is a good candidate for dental sealants. If they are, we can place their sealants right away to help seal off those cavity bugs for good! Don't wait for your child's teeth to develop cavities or infections. Contact us today to see how we can help protect your children's teeth using dental sealants and other preventive dental treatments.
Interested in purchasing treatment directly online? Click on the link below to go to my online store now:
Definition of General Dentistry Terminology
Abscess (cyst)
A pus pocket containing harmful bacteria that forms around infected teeth. Teeth with abscess are considered infected and they either need root canal treatment or must be extracted.
Amalgam (silver filling)
Material used to fill dental cavities. Amalgam is silver colored and contains Mercury. As a filling material, Amalgam is durable and effective. However, there are some concerns about the safety of using Mercury to restore teeth.
Bicuspid tooth
Refer to premolar tooth please.
Canine tooth (cuspid or eye tooth)
A strong, pointed tooth with a single cusp used to direct other teeth as we chew side-to-side. Canine teeth are very strong and typically outlast all other teeth as we age. We have 4 total canines, teeth numbers: 6, 11, 22 and 27.
Cavity (decay)
A hole inside a tooth created by harmful cavity bugs. Dental cavities can cause slight tooth sensitivity, particularly to cold and sweets. They can also be asymptomatic. If left untreated, dental cavities infiltrate the tooth pulp and cause abscess and infection.
Composite resin (white filling)
Material used to fill dental cavities and broken teeth. Composite resin is safe, effective and matches your tooth color. Cosmetic dentists prefer using composite resins to other filling restoration material due to their natural appearance.
Crown (cap)
A large restoration that replaces the majority of your tooth structure above the gum line. Crowns are used to fix teeth which can no longer be salvaged with a simple filling. Crowns are typically made from gold, porcelain-fused-to-metal or ceramic material.
Decay
Refer to cavity please.
Deep cleaning (scaling & root planning)
A type of dental cleaning which focuses on removing plaque and tartar underneath your gum line. Deep cleanings are used to treat gum disease. Most deep cleanings are performed in multiple sessions and often times require anesthesia.
Dental cleaning
Teeth cleaning performed by your dentist or hygienist. Dental cleaning focuses on removing plaque and tartar which can’t be removed by brushing or flossing alone. Dental cleanings are categorized as simple cleaning or deep cleaning.
Dentin
The middle portion of your tooth which is located above the pulp and underneath the enamel. Unlike enamel, dentin has nerve endings which makes it sensitive to tooth decay.
Denture
Removable, false teeth used to replace your missing natural teeth. Dentures are made from pink and white acrylic. The pink portion secures your dentures in place and the white segment replaces your missing teeth. There are many different types of dentures including full dentures and partial dentures.
Enamel
The very hard outer portion of your tooth. In fact, enamel is the hardest tissue found in our bodies. Enamel protects your tooth from cavities and provides it with the strength to cut and chew food.
Filling
Material used by dentists to replace missing tooth structure. Fillings are used to fix dental cavities and broken teeth. Fillings are made from gold (mostly obsolete), Amalgam (silver filling) or composite resin (white filling).
Full Denture (Complete denture)
A set of false teeth which replaces all of your teeth in one arch. Full dentures are held in place by the suction they provide against your gum tissue. Full dentures are typically made from pink and white acrylic.
Gingivitis
The earlier stage of gum disease. Gingivitis is characterized by bleeding gums, bad breath and minor tooth sensitivity. If left untreated, gingivitis progresses to the more advanced stage of gum disease known as periodontitis.
Gum Disease (Periodontal disease)
Disease of the gums and jaw bone. Gum disease is caused by spread of harmful bacteria to your gum and jaw bone. Gum disease causes bleeding gums, bone loss and tooth loss. Gum disease is categorized as gingivitis and periodontitis.
Impacted Tooth
A tooth which is trapped underneath your jaw bone. Impacted tooth typically refers to wisdom teeth, although other teeth can also be impacted. Impacted wisdom teeth usually need to be removed. Other impacted teeth need to be removed, monitored or uprighted by your orthodontist.
Incisor tooth
The front most four teeth in your upper and lower jaw. Incisor teeth are used to cut food particles. We have 8 total incisors, teeth numbers: 7, 8, 9, 10, 23, 24, 25 and 26.
Infection
Spread of harmful bacteria into your tooth nerve. Once cavity bugs reach your tooth nerve, the tooth is now infected. Infected teeth can only be fixed with a root canal or you must remove the tooth completely.
Inlay
A type of crown which is a hybrid between fillings and crowns. Inlays are essentially conservative crowns which protect teeth similar to a crown but are conservative similar to a filling. Inlays are smaller than onlays and do not encompass your outer tooth walls.
Molar tooth
Teeth located in the back of our mouth which have four cusps. Molar teeth are large and used to crush food particles. We have 8 total molars, teeth numbers: 2, 3, 14, 15, 18, 19, 30 and 31. Additionally, some of us have 3rd molars or wisdom teeth which are teeth numbers: 1, 16, 17 and 32.
Nerve
Refer to pulp please.
Night guard
A device worn at nights to protect your teeth against grinding. Night guards help reduce tooth fracture, TMJ pain and headaches. There are two types of night guards, generic night guards which you purchase online or from a local pharmacy and custom night guards which your dentist makes for you.
Onlay
A type of crown which is a hybrid between fillings and crowns. Onlays are essentially conservative crowns which protect teeth similar to a crown but are conservative similar to a filling. Onlays are larger than inlays and encompass at least one or more of your outer tooth walls.
Partial Denture
A set of false teeth which replaces some, but not all, of your missing teeth. Partial dentures are held in place by anchoring to your remaining teeth as well as suction against your gum tissue. Partial dentures can be made from different material including metals, acrylic and flexible resin.
Periodontal disease
Refer to gum disease please.
Periodontitis
The more advanced stage of gum disease. Periodontitis is characterized by bone loss, major tooth sensitivity and loose teeth. If left untreated, periodontitis causes your teeth to loosen and fall out. Plus, the resulting infection can spread to the rest of your body and affect your overall health.
Premolar tooth (bicsupid)
Transitional teeth between our front and molar teeth. Premolars have two cusps and are used to crush food particles. They are also the teeth most commonly removed for braces treatment. We have 8 total bisupids, teeth numbers: 4, 5, 12, 13, 20, 21, 28 and 29.
Pulp (nerve)
The innermost tooth layer which lies underneath your dentin. Your tooth pulp contains nerves and blood vessels. When your tooth pulp becomes damaged this results in a toothache. Once this happens, you require a root canal treatment or must remove the tooth.
Pulpotomy
Pulpotomy is the equivalent of a baby root canal. It entails removing the nerve structure from infected baby teeth. Performing a pulpotomy eliminates toothache while allowing your child to keep the tooth itself in order to prevent potential orthodontic complications.
Root canal treatment
A procedure to remove infected tooth nerve to eliminate pain and infection. During root canal treatment your dentist will disinfect your tooth and replace the missing nerve with sterile material known as Gutta Percha. Root canal treatment eliminates pain and infection and allows you to keep the tooth.
Scaling & root planning
Refer to deep cleaning please.
Sealant
A preventive treatment used to protect children’s teeth. Dental sealants are placed on teeth with deep groves, typically molars, to protect them against tooth decay and infection. Sealants are very effective and safe and do not require any tooth structure removal.
Sedation
Techniques used to calm patients with anxiety during dental treatment. There are many different sedation techniques in dentistry such as Nitrous Oxide, oral conscious sedation, IV sedation and general anesthesia.
Silver filling
Refer to Amalgam please.
Simple cleaning
A dental cleaning performed in absence of gum disease. Simple cleanings typically entail basic tooth scraping and polishing, occasionally with Fluoride treatment. Most people require a simple cleaning once every 6 months, although if you’re suffering from gum disease you need one every 3 to 4 months.
Third molar
Refer to wisdom tooth please.
White filling
Refer to composite resin please.
Wisdom tooth (third molar)
Tooth which is located all the way in the back of your mouth. Wisdom teeth start erupting in your late teens or twenties. Not everyone has wisdom teeth. For those that do, there’s a high probability that you have to remove these teeth. Otherwise, they will cause pain, swelling and infection.
Oceansight Dental & Implants
General, Cosmetic & Implant Dentistry
Office of Ali John Jazayeri
133 Avenida Granda
San Clemente, CA 92672
